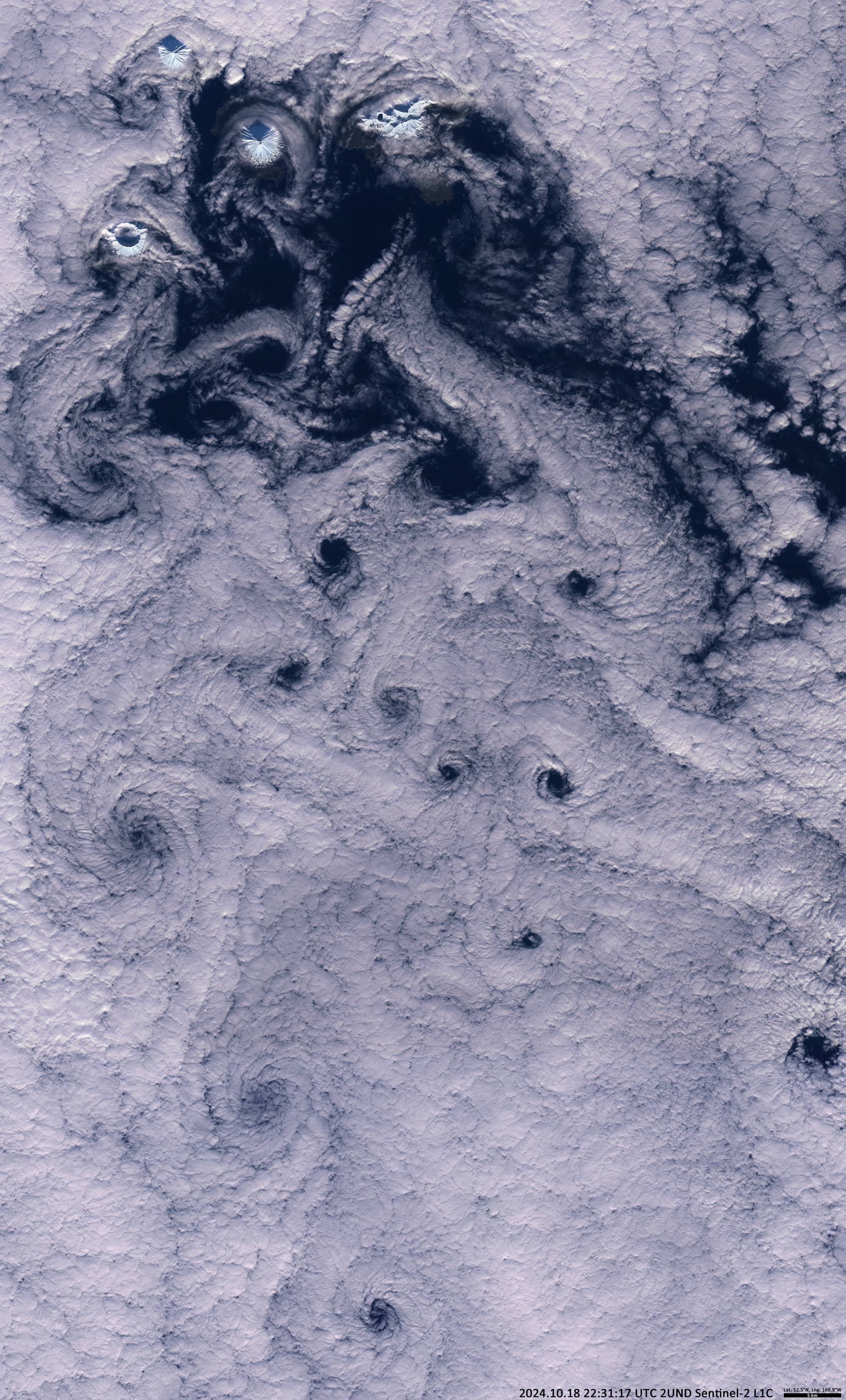
Clouds over Uniiĝun Islands
Aleutian Islands | Western Alaska
Dates of acquisition:
October 18th, 2024 | 22:31:17 UTC
October 21st, 2024 | 22:41:14 UTC
Sensor: Sentinel-2 L1C
Coordinates: ca. 52.5°N, 169.8°W
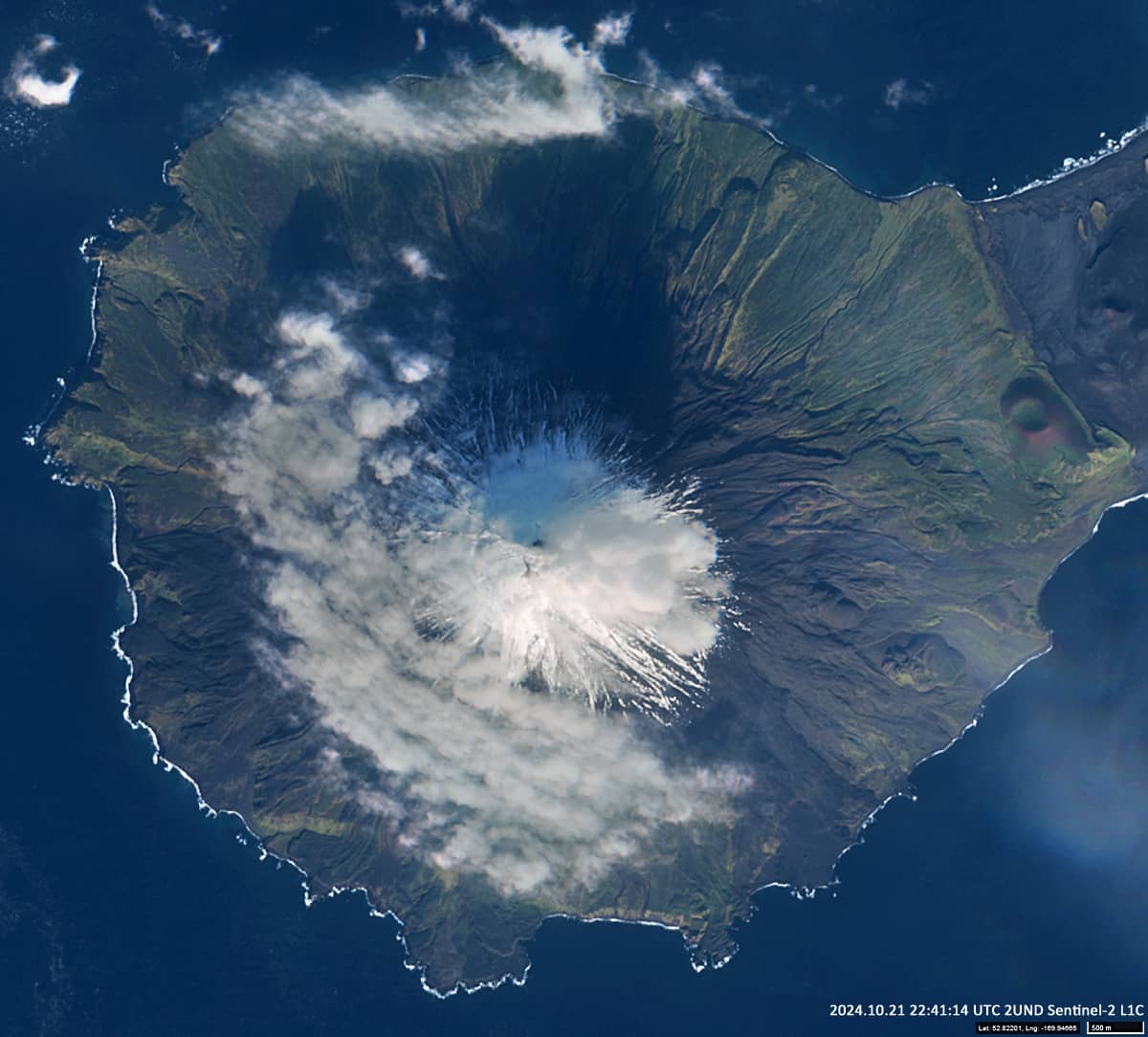
The satellite image shows cloud structures that have formed south of the Uniiĝun Islands (The Islands of Four Mountains), which are part of the Aleutian Island Arc (Figure 1). From west to east are the islands of Herbert (highest point 1280 m above sea level), Carlisle (crater elevation 1610 m) and Chuginadak with one of the most active volcanoes in the world – Cleveland volcano (1730 m above sea level).
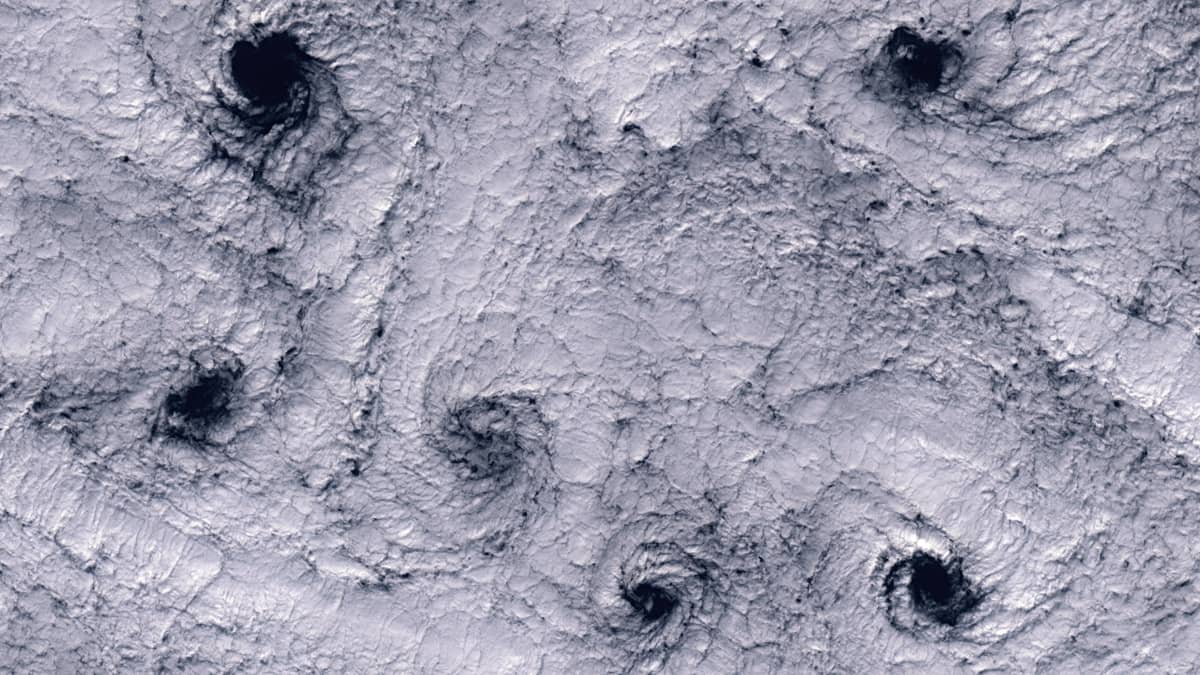
The swirling cloud structures are caused by turbulences in the air, called Karman vortices. The cold wind from the Bering Sea bends around the cone-shaped volcanoes, which act as obstacles, and creates vortices on the leeward, southern side of the islands.
The cloud top height is below 1200 m and the clouds act as a kind of marker for the air currents.
The sun shines from the south and, due to the presence of low clouds, casts delta-shaped shadows on the opposite windward, northern side of the volcanic cone. Figure 2 shows Cleveland Volcano three days later.